Configuration
Jenkins operator uses job-dsl and kubernetes-credentials-provider plugins for configuring jobs and deploy keys.
Prepare job definitions and pipelines
First you have to prepare pipelines and job definition in your GitHub repository using the following structure:
cicd/
├── jobs
│ └── build.jenkins
└── pipelines
└── build.jenkinscicd/jobs/build.jenkins it’s a job definition:
#!/usr/bin/env groovy
pipelineJob('build-jenkins-operator') {
displayName('Build jenkins-operator')
definition {
cpsScm {
scm {
git {
remote {
url('https://github.com/jenkinsci/kubernetes-operator.git')
credentials('jenkins-operator')
}
branches('*/master')
}
}
scriptPath('cicd/pipelines/build.jenkins')
}
}
}cicd/pipelines/build.jenkins is an actual Jenkins pipeline:
#!/usr/bin/env groovy
def label = "build-jenkins-operator-${UUID.randomUUID().toString()}"
def home = "/home/jenkins"
def workspace = "${home}/workspace/build-jenkins-operator"
def workdir = "${workspace}/src/github.com/jenkinsci/kubernetes-operator/"
podTemplate(label: label,
containers: [
containerTemplate(name: 'jnlp', image: 'jenkins/inbound-agent:alpine'),
containerTemplate(name: 'go', image: 'golang:1-alpine', command: 'cat', ttyEnabled: true),
],
envVars: [
envVar(key: 'GOPATH', value: workspace),
],
) {
node(label) {
dir(workdir) {
stage('Init') {
timeout(time: 3, unit: 'MINUTES') {
checkout scm
}
container('go') {
sh 'apk --no-cache --update add make git gcc libc-dev'
}
}
stage('Dep') {
container('go') {
sh 'make dep'
}
}
stage('Test') {
container('go') {
sh 'make test'
}
}
stage('Build') {
container('go') {
sh 'make build'
}
}
}
}
}Configure Seed Jobs
Jenkins Seed Jobs are configured using Jenkins.spec.seedJobs section from your custom resource manifest:
apiVersion: jenkins.io/v1alpha2
kind: Jenkins
metadata:
name: example
spec:
seedJobs:
- id: jenkins-operator
targets: "cicd/jobs/*.jenkins"
description: "Jenkins Operator repository"
repositoryBranch: master
repositoryUrl: https://github.com/jenkinsci/kubernetes-operator.gitJenkins Operator will automatically discover and configure all the seed jobs.
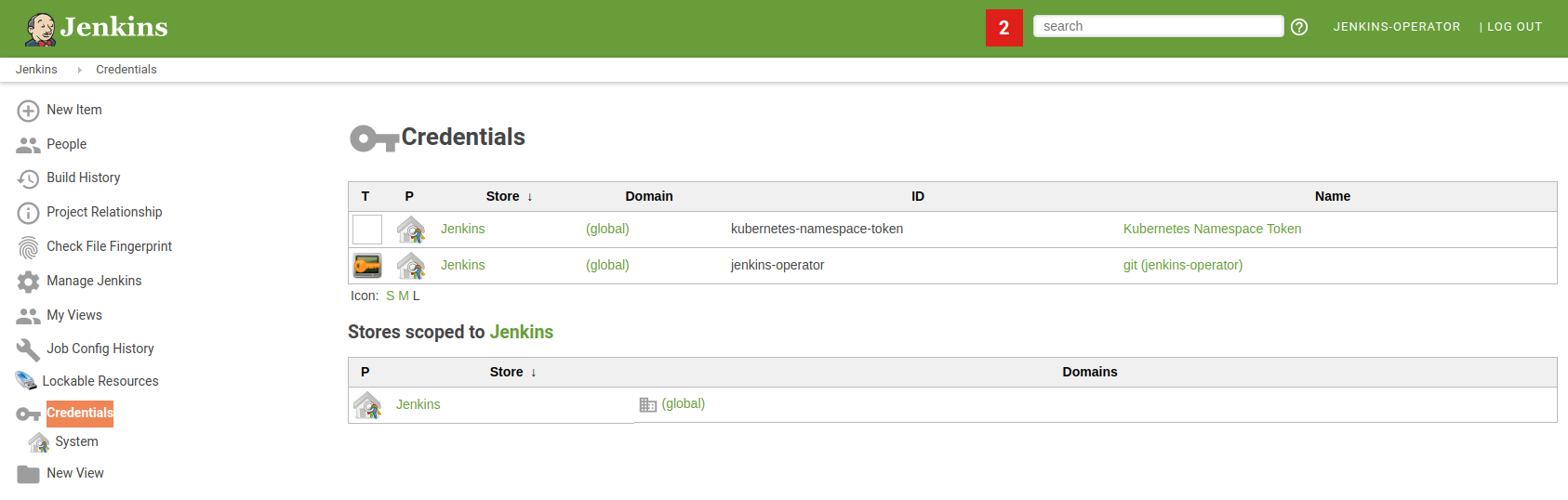
You can verify if deploy keys were successfully configured in the Jenkins Credentials tab.
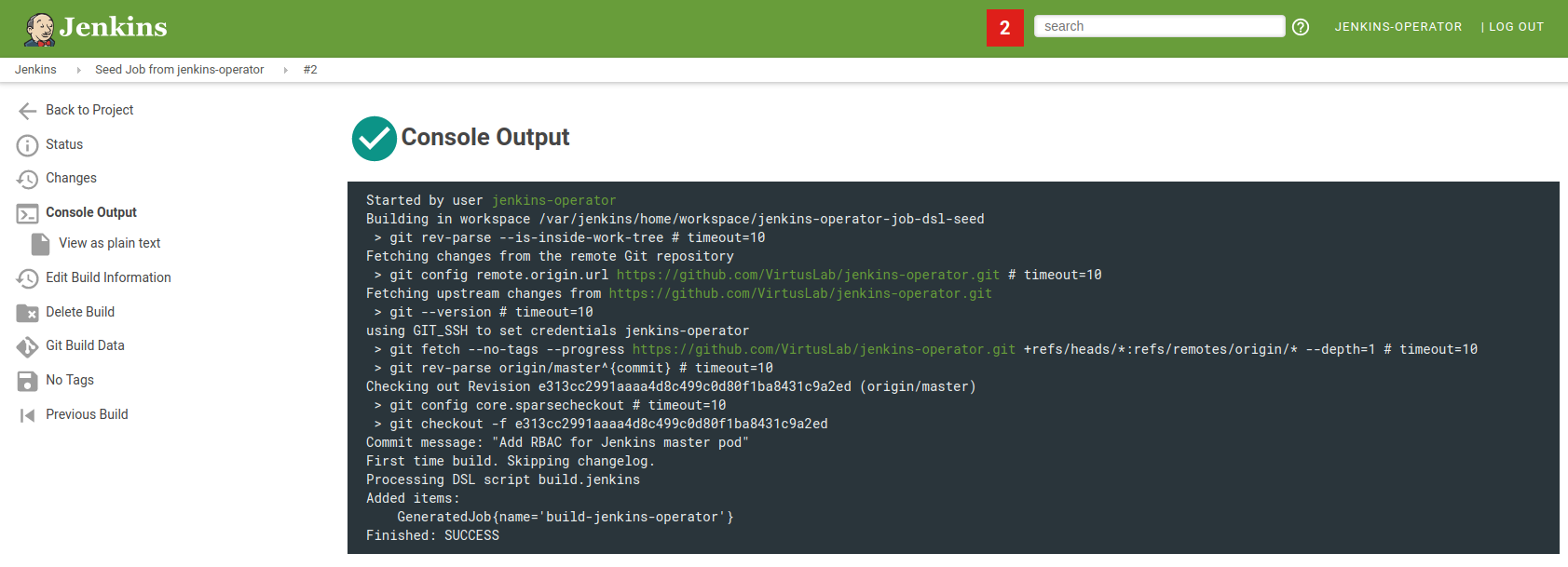
You can verify if your pipelines were successfully configured in the Jenkins Seed Job console output.
If your GitHub repository is private you have to configure SSH or username/password authentication.
SSH authentication
Generate SSH Keys
There are two methods of SSH private key generation:
$ openssl genrsa -out <filename> 2048or
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 2048
$ ssh-keygen -p -f <filename> -m pemThen copy content from generated file.
Public key
If you want to upload your public key to your Git server you need to extract it.
If key was generated by openssl then you need to type this to extract public key:
$ openssl rsa -in <filename> -pubout > <filename>.pubIf key was generated by ssh-keygen the public key content is located in
Configure SSH authentication
Configure a seed job like this:
apiVersion: jenkins.io/v1alpha2
kind: Jenkins
metadata:
name: example
spec:
seedJobs:
- id: jenkins-operator-ssh
credentialType: basicSSHUserPrivateKey
credentialID: k8s-ssh
targets: "cicd/jobs/*.jenkins"
description: "Jenkins Operator repository"
repositoryBranch: master
repositoryUrl: git@github.com:jenkinsci/kubernetes-operator.gitand create a Kubernetes Secret (name of secret should be the same from credentialID field):
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: k8s-ssh
stringData:
privateKey: |
-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
MIIJKAIBAAKCAgEAxxDpleJjMCN5nusfW/AtBAZhx8UVVlhhhIKXvQ+dFODQIdzO
oDXybs1zVHWOj31zqbbJnsfsVZ9Uf3p9k6xpJ3WFY9b85WasqTDN1xmSd6swD4N8
...
username: github_user_nameUsername & password authentication
Configure a seed job like this:
apiVersion: jenkins.io/v1alpha2
kind: Jenkins
metadata:
name: example
spec:
seedJobs:
- id: jenkins-operator-user-pass
credentialType: usernamePassword
credentialID: k8s-user-pass
targets: "cicd/jobs/*.jenkins"
description: "Jenkins Operator repository"
repositoryBranch: master
repositoryUrl: https://github.com/jenkinsci/kubernetes-operator.gitand create a Kubernetes Secret (name of secret should be the same from credentialID field):
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: k8s-user-pass
stringData:
username: github_user_name
password: password_or_tokenHTTP Proxy for downloading plugins
To use forwarding proxy with an operator to download plugins you need to add the following environment variable to Jenkins CR, for e.g.:
spec:
master:
containers:
- name: jenkins-master
env:
- name: CURL_OPTIONS
value: -L -x <proxy_url>In CURL_OPTIONS var you can set additional arguments to curl command.
Jenkins login credentials
The operator automatically generates a Jenkins username and password and stores it in Kubernetes secret named
jenkins-operator-credentials-<cr_name> in the namespace where Jenkins CR has been deployed.
If you want change it you can override the secret:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: jenkins-operator-credentials-<cr-name>
namespace: <namespace>
data:
user: <base64-encoded-new-username>
password: <base64-encoded-new-password>If needed Jenkins Operator will restart the Jenkins master pod and then you can login with the new username and password credentials.
Override default Jenkins container command
The default command for the Jenkins master container jenkins/jenkins:lts looks like:
command:
- bash
- -c
- /var/jenkins/scripts/init.sh && /usr/bin/tini -s -- /usr/local/bin/jenkins.shThe script/var/jenkins/scripts/init.sh is provided by the operator and configures init.groovy.d (creates the Jenkins user)
and installs plugins.
The /usr/bin/tini -s -- /usr/local/bin/jenkins.sh command runs the Jenkins master main process.
You can overwrite it in the following pattern:
command:
- bash
- -c
- /var/jenkins/scripts/init.sh && <custom-code-here> && /usr/bin/tini -s -- /usr/local/bin/jenkins.sh