Architecture and design
Jenkins Operator fundamentals
The Jenkins Operator design incorporates the following concepts:
- watches any changes of manifests and maintain the desired state according to deployed custom resource manifest
- implements the main reconciliation loop which consists of two smaller reconciliation loops - base and user
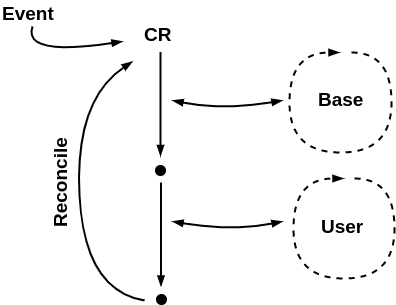
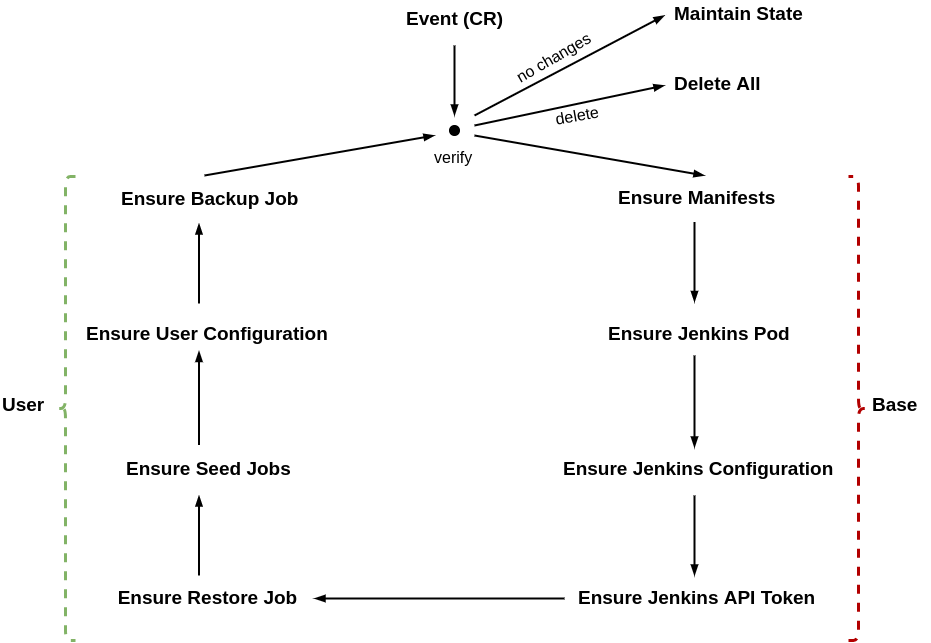
Base reconciliation loop takes care of reconciling base Jenkins configuration, which consists of:
- Ensure Manifests - monitors any changes in manifests
- Ensure Jenkins Pod - creates and verifies the status of Jenkins master Pod
- Ensure Jenkins Configuration - configures Jenkins instance including hardening, initial configuration for plugins, etc.
- Ensure Jenkins API token - generates Jenkins API token and initialized Jenkins client
User reconciliation loop takes care of reconciling user provided configuration, which consists of:
- Ensure Restore Job - creates Restore job and ensures that restore has been successfully performed
- Ensure Seed Jobs - creates Seed Jobs and ensures that all of them have been successfully executed
- Ensure User Configuration - executed user provided configuration, like groovy scripts, configuration as code or plugins
- Ensure Backup Job - creates a Backup job and ensures that backup has been successfully performed
Operator State
Operator state is kept in the custom resource status section, which is used for storing any configuration events or job statuses managed by the operator.
It helps to maintain or recover the desired state even after the operator or Jenkins restarts.
Webhook
It rejects/accepts admission requests based on potential security warnings in plugins present in the Jenkins Custom Resource.
Last modified October 1, 2021