Running the Jenkins Container¶
Docker simplifies packaging applications with all their dependencies.
Through Docker, we can have a running Jenkins instance in a matter of seconds.
In your terminal, first build a Jenkins image with docker installed. Create a Dockerfile in an empty directory with the following:
FROM jenkins/jenkins:lts
USER root
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y \
apt-transport-https \
ca-certificates \
curl \
gnupg-agent \
software-properties-common
RUN curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/debian/gpg | apt-key add
RUN add-apt-repository \
"deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/debian \
$(lsb_release -cs) \
stable"
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
EXPOSE 8080
From the same directory as your Dockerfile, build the image:
docker build -t jenkins:lts-docker .
Note
Running Jenkins as a docker container on a BAH-managed machine requires specific certificates and tooling to be installed. A Dockerfile meeting these requirements can be built from the solutions-delivery-platform/bah-jenkins repository.
Then, to start Jenkins, run:
On Linux or Mac:
docker run --name jenkins \
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \
--privileged \
--user root \
-p 50000:50000 \
-p 8080:8080 \
-d \
jenkins:lts-docker
On Windows:
docker run --name jenkins \
-v //var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \
--privileged \
--user root \
-p 50000:50000 \
-p 8080:8080 \
-d \
jenkins:lts-docker
Command Line Breakdown¶
| Command Section | Description |
|---|---|
docker run |
Tells Docker to run a command in a new container. |
--name jenkins |
Names the container being launched jenkins. This is done for ease of referencing it later. |
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock |
Mounts the local Docker daemon socket to the Jenkins container. |
–-privileged |
Escalates the container permissions so it can launch containers on the host docker daemon. |
–-user root |
Runs the container as the root user so it can launch containers on the host docker daemon. |
-p 50000:50000 |
Port forwarding of the default JNLP agent port to our localhost. |
-p 8080:8080 |
Port forwarding of the Jenkins port to our localhost. |
-d |
Runs the container process in the background. |
jenkins:lts-docker |
The container image from which to run this container. |
Note
If port 8080 is already in use by another process then this command will fail. To run Jenkins on a different port, swap out the first 8080 to your desired port: <desired port number>:8080.
You can run docker logs -f jenkins to see the Jenkins logs. It will say "Jenkins is fully up and running" when Jenkins is ready.
You can validate the container launched as expected by going to http://localhost:8080.
You should see the Jenkins Startup Wizard:
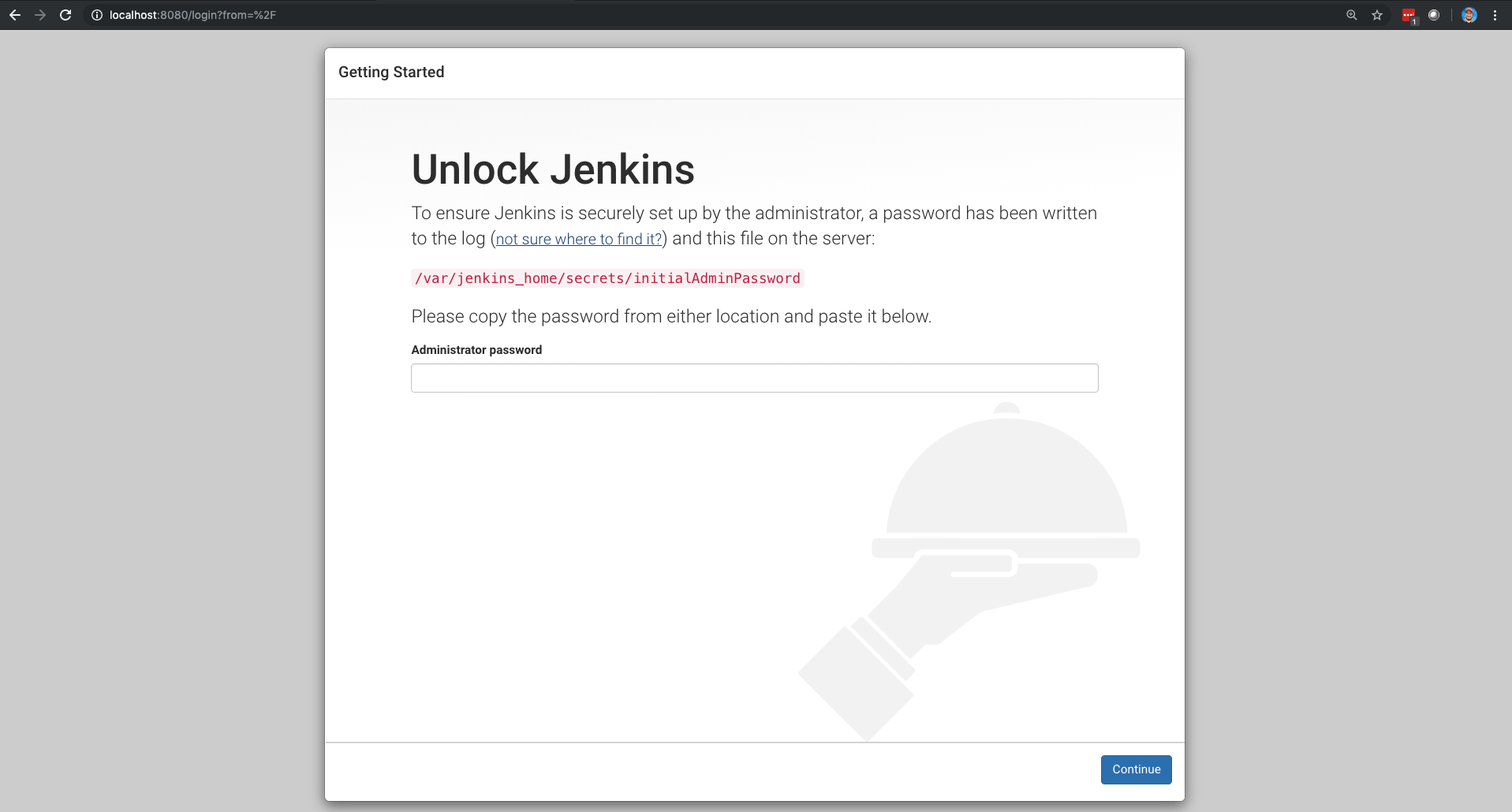
In the next section, we'll learn how to get past this Startup Wizard and configure the newly deployed Jenkins instance.